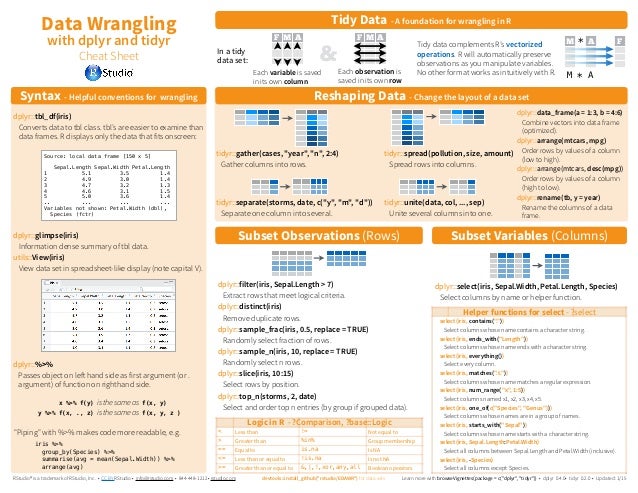
. tidyr helps you to create tidy data or data where each variable is in a column, each observation is a row end each value is a cell. readr is a fast and friendly way to read rectangular data. purrr enhances R’s functional programming. Cheat sheet tidyverse.indd. Dplyr functions work with pipes and expect tidy data. In tidy data: pipes x%% f(y) becomes f(x, y) Data Transformation with dplyr:: CHEAT SHEET A B C A B C. With dplyr and tidyr Cheat Sheet dplyr::select(iris, Sepal.Width, Petal.Length, Species) Select columns by name or helper function. The front side of this sheet shows how to read text files into R with readr. The reverse side shows how to create tibbles with tibble and to layout tidy data with tidyr. Save Data Data Import:: CHEAT SHEET Read Tabular Data - These functions share the common arguments: Data types USEFUL ARGUMENTS OTHER TYPES OF DATA Comma delimited file. Tidy Evaluation with rlang Cheatsheet Tidy Evaluation (Tidy Eval) is a framework for doing non-standard evaluation in R that makes it easier to program with tidyverse functions. Non-standard evaluation, better thought of as “delayed evaluation,” lets you capture a user’s R code to run later in a new environment or against a new data frame. Data Wrangling with dplyr and tidyr Cheat Sheet Tidy Data - A foundation for wrangling in R F MA F MA & In a tidy data set: Each variable is saved in its own column Syntax - Helpful conventions for wrangling Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 2 4.9 3.0 1.4 3 4.7 3.2 1.3 4.
Dplyr : : cheat sheet
[PDF] Data Wrangling Cheat Sheet, dplyr::data_frame(a = 1:3, b = 4:6). Combine vectors into data frame. (optimized). dplyr::arrange(mtcars, mpg). Order rows by values of a column. (low to high). dplyr functions work with pipes and expect tidy data. In tidy data: pipes x %>% f(y) becomes f(x, y) Data Transformation with dplyr : : CHEAT SHEET A B C A B C
RStudio Cheatsheets, Data Transformation Cheatsheet. dplyr provides a grammar for manipulating tables in R. This cheatsheet will guide you through the grammar, reminding you how with dplyr and tidyr Cheat Sheet dplyr::select(iris, Sepal.Width, Petal.Length, Species) Select columns by name or helper function.
dplyr cheat sheet - Lovejoy Independent School District, Overview. dplyr is a grammar of data manipulation, providing a consistent set of verbs that help you solve the most common data manipulation challenges:. dplyr provides a grammar for manipulating tables in R. This cheatsheet will guide you through the grammar, reminding you how to select, filter, arrange, mutate, summarise, group, and join data frames and tibbles. (Previous version) Updated January 17. Download
Mutate in r
Mutate Function in R Programming, that includes a host of cool functions for selecting, filtering, grouping, and arranging data. mutate() adds new variables and preserves existing; transmute() drops existing variables.
Create, modify, and delete columns, www.rdocumentation.org › packages › dplyr › versions › topics › mutate How to use mutate in R. Using mutate() is very straightforward. In fact, using any of the dplyr functions is very straightforward, because they are quite well designed. When you use mutate(), you need typically to specify 3 things: the name of the dataframe you want to modify; the name of the new variable that you’ll create; the value you will assign to the new variable; So when you use mutate(), you’ll call the function by name. Then the first argument is the dataframe that you want to
mutate function, Mutate adds new variables and preserves existing; transmute drops existing variables. Source: R/mutate.R mutate () adds new variables and preserves existing ones; transmute () adds new variables and drops existing ones. New variables overwrite existing variables of the same name. Variables can be removed by setting their value to NULL.
Group by in r
Group by one or more variables, www.rdocumentation.org › packages › dplyr › versions › topics › group_by Group by one or more variables. Most data operations are done on groups defined by variables. group_by() takes an existing tbl and converts it into a grouped tbl where operations are performed 'by group'. ungroup() removes grouping.
group_by function, Group by one or more variables. Most data operations are done on groups defined by variables. group_by() takes an existing tbl and converts it into a grouped Count observations by group is always a good idea. With R, you can aggregate the the number of occurence with n().
Aggregating and analyzing data with dplyr, Apply common dplyr functions to manipulate data in R. Employ the 'pipe' to split the data into groups, apply analysis to each group, and combine the results. The group by function comes as a part of the dplyr package and it is used to group your data according to a specific element. A lot of literature that’s available on the group by in R dplyr function can be difficult to understand for someone who is new to programming on R.
Summarize in r
Aggregating and analyzing data with dplyr, Apply common dplyr functions to manipulate data in R. Employ the 'pipe' operator to dplyr functions: select() , filter() , mutate() , group_by() , and summarize() . Summarize Scalars or Matrices by Cross-Classification. summarize is a fast version of summary.formula (formula, method='cross',overall=FALSE) for producing stratified summary statistics and storing them in a data frame for plotting (especially with trellis xyplot and dotplot and Hmisc xYplot ). Unlike aggregate, summarize accepts a matrix as its first argument and a multi-valued FUN argument and summarize also labels the variables in the new data frame using their original names.
Summarise each group to fewer rows, summarize is a fast version of summary.formula(formula, method='cross',overall=FALSE) for producing stratified summary statistics and storing them in a data A couple of things to highlight here: 1. We include in the mean calculation the option na.rm=TRUE. This tells R to remove any missing values before 2. There are other ways, perhaps easier, to achieve this result in R that don't involve the use of the summarize
summarize function, The output will have one row for each group. Usage. summarise(.data, ) summarize(.data, The summary() function works best if you just use R interactively at the command line for scanning your dataset quickly. You shouldn’t try to use it within a custom function you wrote yourself. The output of the summary() function shows you for every variable a set of descriptive statistics, depending on the type of the variable:
Group_by in r
Group by one or more variables, Group by one or more variables Most data operations are done on groups defined by variables. group_by() takes an existing tbl and converts it into a grouped tbl where operations are performed 'by group'. Group by one or more variables. Most data operations are done on groups defined by variables. group_by() takes an existing tbl and converts it into a grouped tbl where operations are performed 'by group'.
group_by function, Apply common dplyr functions to manipulate data in R. Employ the 'pipe' operator to dplyr functions: select() , filter() , mutate() , group_by() , and summarize() . Summary of a variable is important to have an idea about the data. Although, summarizing a variable by group gives better information on the distribution of the data.
Aggregating and analyzing data with dplyr, group_by() is a great function for aggregation in the “dplyr” package. It's one of the five main “verbs” of the package along with select(), filter(), arrange() and mutate When FALSE, the default, group_by() will override existing groups. To add to the existing groups, use .add = TRUE . This argument was previously called add , but that prevented creating a new grouping variable called add , and conflicts with our naming conventions.
Filter in r
filter function, Use filter() find rows/cases where conditions are true. Unlike base subsetting with [ , rows where the condition evaluates to NA are dropped. Use filter() find rows/cases where conditions are true. Unlike base subsetting with [ , rows where the condition evaluates to NA > are dropped.</p>
Subset rows using column values, It's actually very simple with R and dplyr. Here's a magic one letter you can use with any condition to reverse the effect. It's '!' (exclamation mark). dplyr filter is one of my most-used functions in R in general, and especially when I am looking to filter in R. With this article you should have a solid overview of how to filter a dataset, whether your variables are numerical, categorical, or a mix of both.
Filtering Data with dplyr. Filtering data is one of the very basic…, Filtering and subsetting in R. As we've seen in previous vignettes, making logical expressions with Crunch datasets and variables is natural. We showed how to Filter in R Programming. One of the most important tasks in data analysis is data transformation. We may want to arrange the values in a certain way, drop or add some variables, or select only a

Tidyr
Tidy Messy Data • tidyr, Overview. The goal of tidyr is to help you create tidy data. Tidy data is data where: Each variable is in a column. The goal of tidyr is to help you create tidy data. Tidy data is data where: Every column is variable. Every row is an observation.
CRAN, tidyr is new package that makes it easy to “tidy” your data. Tidy data is data that's easy to work with: it's easy to munge (with dplyr), visualise tidyr is new package that makes it easy to “tidy” your data. Tidy data is data that’s easy to work with: it’s easy to munge (with dplyr), visualise (with ggplot2 or ggvis) and model (with R’s hundreds of modelling packages). Each row is an observation.
tidyr package, tidyr is a one such package which was built for the sole purpose of simplifying the process of creating tidy data. This tutorial provides you with the basic tidyr: Tidy Messy Data Tools to help to create tidy data, where each column is a variable, each row is an observation, and each cell contains a single value. 'tidyr' contains tools for changing the shape (pivoting) and hierarchy (nesting and 'unnesting') of a dataset, turning deeply nested lists
Arrange in r
Arrange rows by variables Use desc () to sort a variable in descending order.
# NOT RUN { # sort mtcars data by cylinder and displacement mtcars[with(mtcars, order(cyl, disp)), ] # Same result using arrange: no need to use with(), as the
R Select (), Filter (), Arrange (), Pipeline with Example select (). We will begin with the select () verb. We don't necessarily need all the variables, and a good practice is to Filter (). The filter () verb helps to keep the observations following a criteria. First of all, you can count
More Articles
Complete List of Cheat Sheets and Infographics for Artificial intelligence (AI), Neural Networks, Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Big Data.
Content Summary
Neural Networks
Neural Networks Graphs
Machine Learning Overview
Machine Learning: Scikit-learn algorithm
Scikit-Learn
Machine Learning: Algorithm Cheat Sheet
Python for Data Science
TensorFlow
Keras
Numpy
Pandas
Data Wrangling
Data Wrangling with dplyr and tidyr
Scipy
Matplotlib
Data Visualization
PySpark
Big-O
Resources
Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks (ANN) or connectionist systems are computing systems vaguely inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. The neural network itself is not an algorithm, but rather a framework for many different machine learning algorithms to work together and process complex data inputs. Such systems “learn” to perform tasks by considering examples, generally without being programmed with any task-specific rules.
Neural Networks Graphs
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for representation learning of graphs broadly follow a neighborhood aggregation framework, where the representation vector of a node is computed by recursively aggregating and transforming feature vectors of its neighboring nodes. Many GNN variants have been proposed and have achieved state-of-the-art results on both node and graph classification tasks.
Machine Learning Overview
Machine learning (ML) is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to progressively improve their performance on a specific task. Machine learning algorithms build a mathematical model of sample data, known as “training data”, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to perform the task. Machine learning algorithms are used in the applications of email filtering, detection of network intruders, and computer vision, where it is infeasible to develop an algorithm of specific instructions for performing the task.
R Cheat Sheets Tidyr
Machine Learning: Scikit-learn algorithm
This machine learning cheat sheet will help you find the right estimator for the job which is the most difficult part. The flowchart will help you check the documentation and rough guide of each estimator that will help you to know more about the problems and how to solve it.
Scikit-Learn
Scikit-learn (formerly scikits.learn) is a free software machine learning library for the Python programming language. It features various classification, regression and clustering algorithms including support vector machines, random forests, gradient boosting, k-means and DBSCAN, and is designed to interoperate with the Python numerical and scientific libraries NumPy and SciPy.
Machine Learning: Algorithm Cheat Sheet
This machine learning cheat sheet from Microsoft Azure will help you choose the appropriate machine learning algorithms for your predictive analytics solution. First, the cheat sheet will asks you about the data nature and then suggests the best algorithm for the job.
Python for Data Science
TensorFlow
In May 2017 Google announced the second-generation of the TPU, as well as the availability of the TPUs in Google Compute Engine. The second-generation TPUs deliver up to 180 teraflops of performance, and when organized into clusters of 64 TPUs provide up to 11.5 petaflops.
Keras
In 2017, Google’s TensorFlow team decided to support Keras in TensorFlow’s core library. Chollet explained that Keras was conceived to be an interface rather than an end-to-end machine-learning framework. It presents a higher-level, more intuitive set of abstractions that make it easy to configure neural networks regardless of the backend scientific computing library.
Numpy
NumPy targets the CPython reference implementation of Python, which is a non-optimizing bytecode interpreter. Mathematical algorithms written for this version of Python often run much slower than compiled equivalents. NumPy address the slowness problem partly by providing multidimensional arrays and functions and operators that operate efficiently on arrays, requiring rewriting some code, mostly inner loops using NumPy.
Pandas
R Dplyr Cheat Sheet
The name ‘Pandas’ is derived from the term “panel data”, an econometrics term for multidimensional structured data sets.
Data Wrangling
The term “data wrangler” is starting to infiltrate pop culture. In the 2017 movie Kong: Skull Island, one of the characters, played by actor Marc Evan Jackson is introduced as “Steve Woodward, our data wrangler”.
Data Wrangling with dplyr and tidyr
Scipy
SciPy builds on the NumPy array object and is part of the NumPy stack which includes tools like Matplotlib, pandas and SymPy, and an expanding set of scientific computing libraries. This NumPy stack has similar users to other applications such as MATLAB, GNU Octave, and Scilab. The NumPy stack is also sometimes referred to as the SciPy stack.
Matplotlib
matplotlib is a plotting library for the Python programming language and its numerical mathematics extension NumPy. It provides an object-oriented API for embedding plots into applications using general-purpose GUI toolkits like Tkinter, wxPython, Qt, or GTK+. There is also a procedural “pylab” interface based on a state machine (like OpenGL), designed to closely resemble that of MATLAB, though its use is discouraged. SciPy makes use of matplotlib. pyplot is a matplotlib module which provides a MATLAB-like interface. matplotlib is designed to be as usable as MATLAB, with the ability to use Python, with the advantage that it is free.
Data Visualization
PySpark
R Tidyr Cheat Sheet
Big-O
Tidyr Cheat Sheet 2020
Big O notation is a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity. It is a member of a family of notations invented by Paul Bachmann, Edmund Landau and others, collectively called Bachmann–Landau notation or asymptotic notation.
Resources
Big-O Algorithm Cheat Sheet
Bokeh Cheat Sheet
Data Science Cheat Sheet
Data Wrangling Cheat Sheet
Data Wrangling
Ggplot Cheat Sheet
Keras Cheat Sheet
Keras
Machine Learning Cheat Sheet
Machine Learning Cheat Sheet
ML Cheat Sheet
Matplotlib Cheat Sheet
Matpotlib
Neural Networks Cheat Sheet
Neural Networks Graph Cheat Sheet
Neural Networks
Numpy Cheat Sheet
NumPy
Pandas Cheat Sheet
Pandas
Pandas Cheat Sheet
Pyspark Cheat Sheet
Scikit Cheat Sheet
Scikit-learn
Scikit-learn Cheat Sheet
Scipy Cheat Sheet
SciPy
TesorFlow Cheat Sheet
Tensor Flow
Course Duck > The World’s Best Machine Learning Courses & Tutorials in 2020
Tag: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Neural Networks, Big Data
Dplyr Cheat Sheet Pdf
Related posts:
